Decorating the Snakefile¶
In the previous steps, the Snakemake rules were run individually. But what if we want to run all the commands at once? It gets tedious to run each command individually, and we can do that already without Snakemake!
By defining the inputs and outputs for each rule's command(s), Snakemake can figure out how the rules are linked together. The rule structure will now look something like this, where input:, output:, and shell: are Snakemake directives:
rule rule_name:
input:
# input file names must be enclosed in quotes
# multiple inputs should be separated by commas
# the new line for each input is optional
"input file 1",
"input file 2",
"input file 3"
output:
# output file names must be enclosed in quotes
# multiple outputs should be separated by commas
"output file 1",
"output file 2"
shell:
# for multi-line commands
# commands must be enclosed in triple quotes
"""
command_1
command_2
"""
Here, Snakemake interprets the input: and output: sections as Python code, and the shell: section as the bash code that gets run on the command line.
Step 4: Adding output files¶
Let's start with a clean slate.
Warning
Be careful with rm command - it deletes files forever!
Delete any output files you created in the sections above, such that you only have the Snakefile in your directory: rm <file name>.
The output of the download_data rule is SRR2584857_1.fastq.gz. Add this to the rule, note that the output file must be in quotes "":
rule download_data:
output: "SRR2584857_1.fastq.gz"
shell:
"wget https://osf.io/4rdza/download -O SRR2584857_1.fastq.gz"
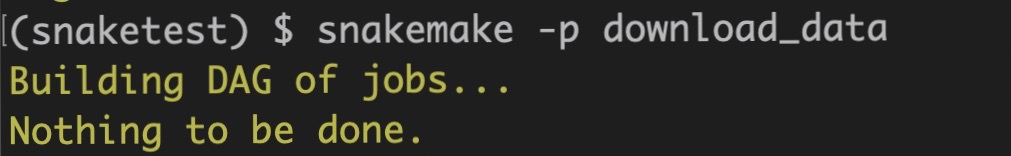
Try: Run the download_data rule twice.
snakemake -p download_data
You will notice the following message after the second run of download_data:
Delete the file: rm SRR2584857_1.fastq.gz. Now run the rule again.
This time the shell command is executed! By explicitly including the output file in the rule, Snakemake was smart enough to know that the output file already exists and doesn't need to be re-created.
Step 5: Adding input files¶
To the download_genome rule, define the following output file:
output: "ecoli-rel606.fa.gz"
To the uncompress_genome rule, add an input and output:
rule uncompress_genome:
input: "ecoli-rel606.fa.gz"
output: "ecoli-rel606.fa"
shell:
"gunzip ecoli-rel606.fa.gz"
What does this do?
The code chunk informs Snakemake that uncompress_genome depends on having the input file ecoli-rel606.fa.gz in the current directory, and that download_genome produces it. Snakemake will automatically determine the dependencies between rules by matching the file name(s).
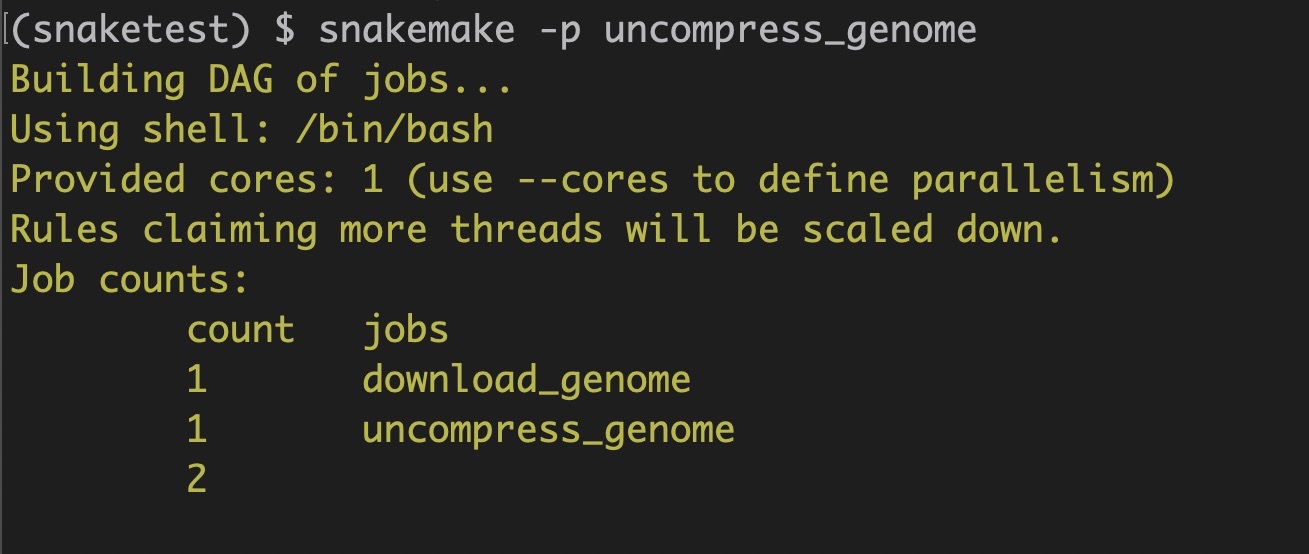
In this case, if we were to run the uncompress_genome rule at the terminal, it will also execute the download_genome rule since the rules are now linked!
snakemake -p uncompress_genome
As expected, two rules are executed in the specified order: first the download_genome followed by uncompress_genome rule.
Key Points
input:andoutput:(and other Snakemake directives) can be written in any order, as long as they are beforeshell:. The Snakemake manual describes other directives you can add to Snakemake rules.- for each of the above elements, their contents can be all on one line, or form a block by indenting
- you can make lists for multiple input or output files by separating filenames with a comma
- rule names can be any valid variable, which basically means letters and underscores; you can use numbers after a first character; no spaces!